Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. However, recent incidents involving EV fires in Korea have raised concerns about the safety of these vehicles. On August 1, 2024, a Mercedes Benz EQE 350+ caught fire in an underground parking lot, and just two weeks later, on August 16, 2024, a Tesla Model X ignited while parked on the side of the road. Two EV fires in such a short time frame are unusual and alarming, prompting us to look closely at the underlying causes.
What Could Be Going Wrong?
While a thorough investigation by Korean authorities is underway, the fires likely originated from faults within the vehicles' batteries. A battery fault can lead to a catastrophic failure that poses a significant risk to human life. Understanding how these failures happen is crucial to managing and mitigating such risks.
The Chain Reaction: How Battery Failures Lead to Fires
A fault in a battery cell can create a chain reaction, resulting in a fire. Here's how it typically unfolds:
Internal Short Circuit: A fault within the battery cell, such as an internal short circuit, triggers an irreversible electrochemical reaction inside the cell.
Gas Venting: This reaction generates gas vented from the cell.
Heat Escalation: As the reaction continues, the cell heats up rapidly, causing materials within the battery to melt.
Thermal Runaway: The heat generated begins to propagate to adjacent cells, triggering a thermal runaway. This is when the heat from one failing cell causes neighboring cells to fail similarly.
Thermal Propagation: As the failure spreads from cell to cell, the entire battery can be consumed in flames.
The Data Analysis Behind the Fires
The critical temperature threshold for triggering thermal runaway in a battery cell is around 120°C. The heat escalates rapidly once this temperature is exceeded, reaching 100°C per second on average. The temperature can soar beyond 500°C, leading to an uncontrollable fire.
The two plots display the cell surface temperature changes during two separate thermal runaway tests for battery cells. These graphs highlight the temperature dynamics during a thermal runaway event, which are influenced by various factors such as battery chemistry, failure mode, and other conditions.

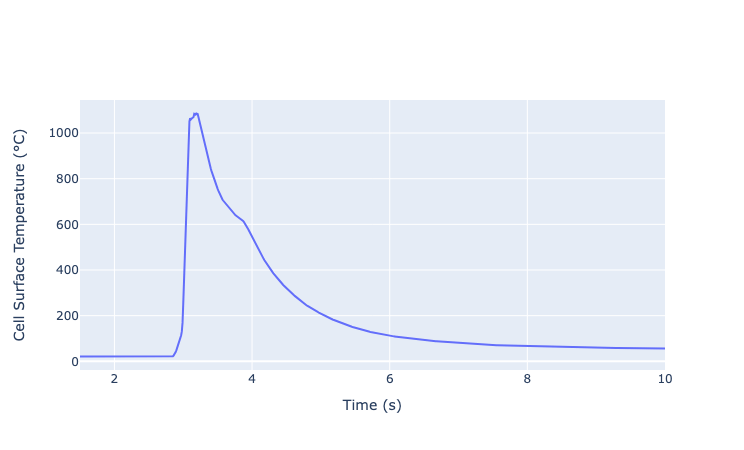
Temperature Increase Dynamics:
The cell temperatures in both plots increase exponentially in the order of seconds, a common characteristic of thermal runaway events. The rapid rise indicates an internal fault or failure mode, causing significant energy release as heat. The variation in peak temperatures—around 600°C in the first plot and over 1000°C in the second—suggests differences in battery chemistry, failure modes, or testing conditions.
Exponential Temperature Rise:
Both graphs show a sharp, exponential temperature rise shortly after the thermal event begins. This pattern is typical in thermal runaway scenarios, where heat generated by an initial failure propagates to adjacent cells, creating a cascading effect. The quick rise to critical levels highlights the need for rapid monitoring and response systems.
Importance of a Fast-Reacting Fail-Safe System:
The steep temperature escalation emphasizes the need for a fail-safe system to react swiftly before the temperature reaches its peak. Delayed detection or response can lead to catastrophic failure and safety hazards. Effective fail-safe systems should detect early signs of failure and activate cooling, isolation, or shutdown procedures immediately to prevent further escalation.
The Importance of Functional Safety
The recent fires highlight the importance of functional safety in EVs. Functional safety involves identifying, measuring, controlling, and managing risks that could cause hazards, such as a battery fire. By understanding the series of events that lead to a catastrophic failure, manufacturers can implement better safety measures to prevent such incidents from occurring.
Conclusion
While the recent EV fires in Korea are concerning, they also serve as a reminder of the importance of ongoing research and development in battery safety. As the industry continues to evolve, ensuring the functional safety of EVs and preventive fail-safe systems will be paramount to maintaining consumer trust and advancing sustainable transportation.